There are a wide range of biomass resources such as forestry residues, municipal solid waste, crop residue, and other organic waste that can be converted into useable forms of energy including heat, electricity, and fuel.
Community scale applications include: biomass, heating systems for residences, schools, government buildings and community centers or district heat plants capable of serving multiple facilities.
Industrial scale applications include: combined heat and power for local industry as well as fuels production and distribution, such as liquid biofuels, biogas and densified wood fuels.
Biomass resource development creates associated jobs, from harvesting and processing to facility operations, fuel sales and distribution.
Types of Biomass
-
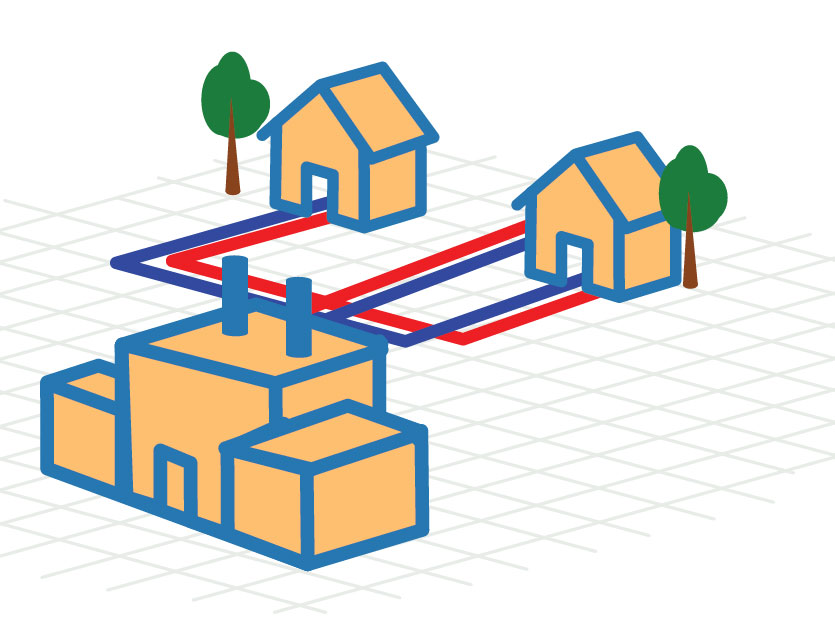
Residential, Commercial & District Heating Alternatives
Wood fuel in the form of logs, chips, and densified pellets and briquettes can be utilized in a plethora of heating applications ranging from supplemental space heating to district heating plants that supply heat to multiple buildings. By using low-cost, locally sourced biomass resources for heating needs, energy cost savings can be realized while keeping money in the community.
-
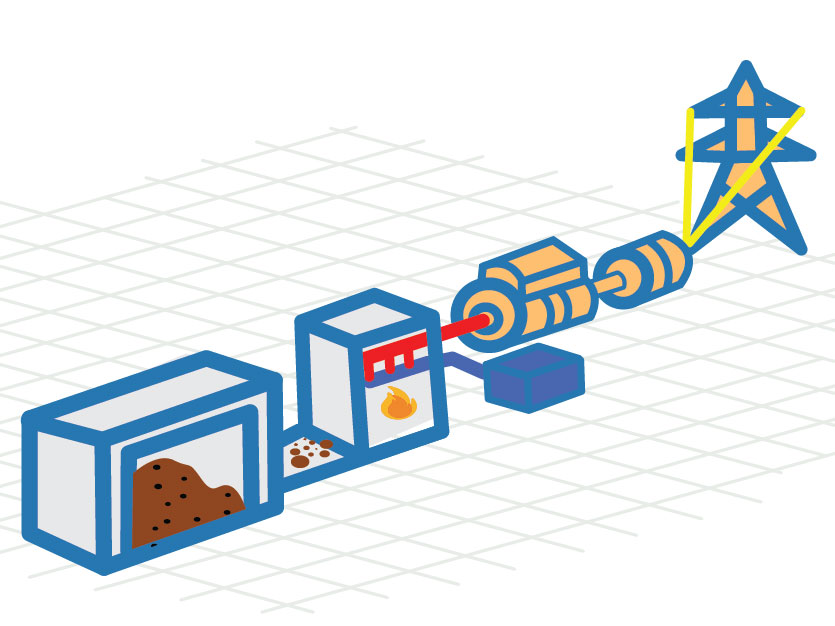
Power Production
Biomass resources such as wood waste, organic solids from municipal waste streams, and crop residues can be utilized to generate electricity through combustion, gasification, anaerobic digestion or pyrolysis. Biomass-generated electricity can be used on-site or sold back to the grid, depending on local utility mandates.
-
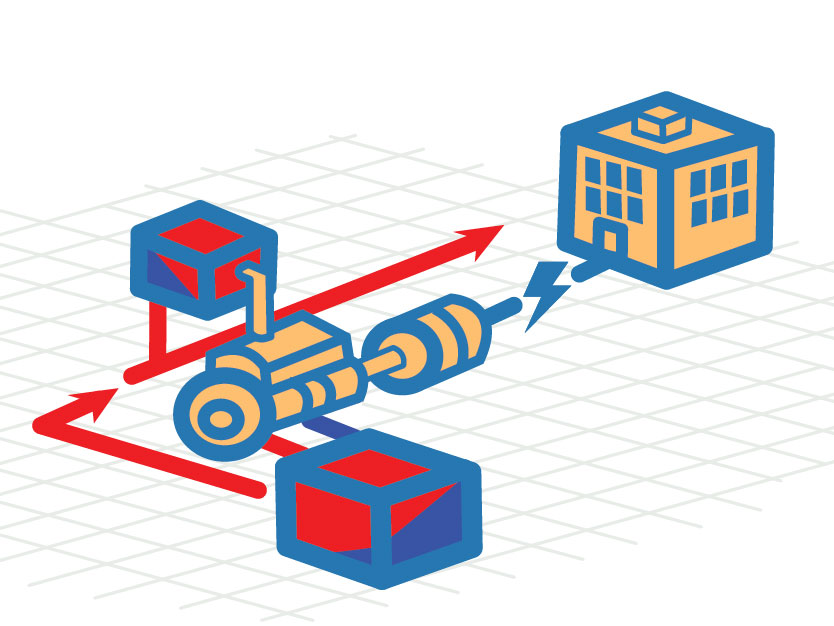
Combined Heat & Power (CHP)
Also known as co-generation, biomass resources can also be utilized to produce both electricity and heat. CHP is typically deployed for on-site consumption, providing electricity and useful heat in industrial, large commercial, and institutional applications. Because CHP technology captures and distributes waste heat associated with electricity production, CHP applications operate at a much higher efficiency, but do require a significant up-front cost to develop.
-
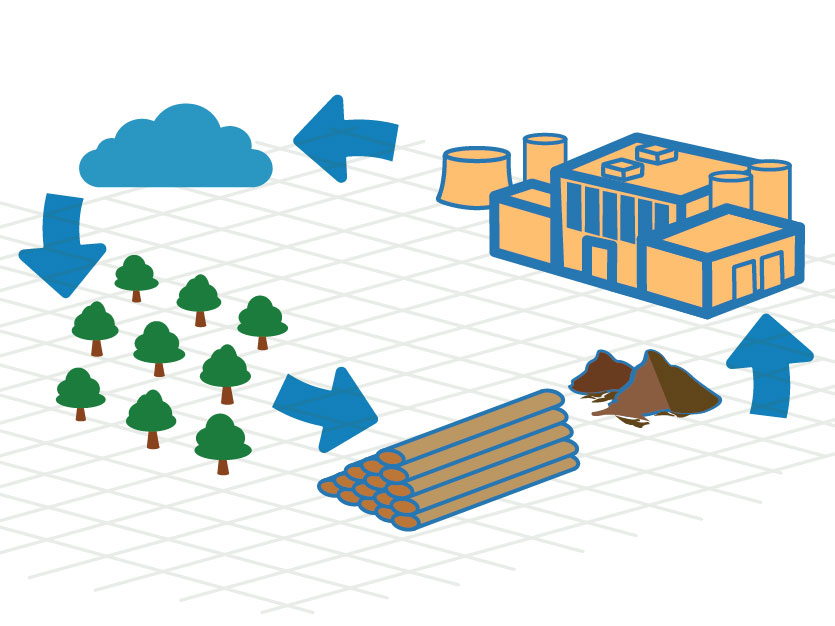
Wildfire Mitigation – Energy Production
Many Tribal nations are located in areas that are increasingly being threatened by wildfire, partially due to a lack of resources needed to maintain forest management and fuel treatment practices. Biomass resource development strategies can provide solutions to these issues, all while adding value by converting biomass to thermal energy and/or electricity and creating needed jobs.
What You Need
For biomass projects to be viable for Tribes, the following characteristics and circumstances must generally be present:
- Stable, low-cost supply of biomass material, responsibly sourced and aligned with sustainable energy objectives.
- Proximity to fuel source; low-cost transportation of raw material to production facilities.
- Access to markets for heat, electricity, or biofuels.
- Current reliance on expensive energy.
- High heat demand.
- Favorable regulatory framework, specifically net-zero emissions policies inclusive to biomass energy resources.
Services for Biomass
The Division of Energy and Mineral Development provides project assistance to Tribes and individuals to develop biomass on their trust land. Learn more about how we can help below.
Additional Information
Additional Resources
Contact Us
Lakewood, CO 80401-3142